History and ethical principles sbe – History and ethical principles in sustainable business enterprise (SBE) form a critical foundation for responsible and ethical business practices. Understanding the evolution and core principles of SBE ethics is essential for navigating complex ethical dilemmas and making informed decisions in today’s business landscape.
This comprehensive overview delves into the historical timeline, fundamental principles, ethical challenges, and professional codes of conduct that shape ethical decision-making in SBE. It also explores emerging ethical issues, comparative ethical frameworks, and ethical considerations in international SBE projects.
1. Historical Overview of Ethical Principles in SBE: History And Ethical Principles Sbe
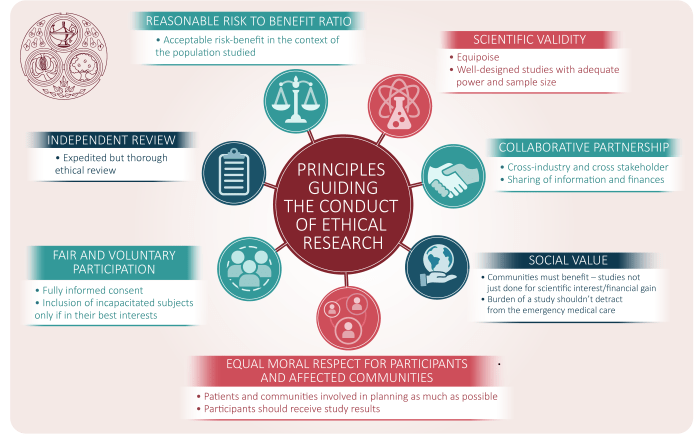
Ethical principles in Sustainable Built Environments (SBE) have evolved significantly over time, reflecting changing societal values and technological advancements.
Key Milestones and Influential Figures
- 1972: Stockholm Conference on the Human Environment: Raised awareness of environmental degradation and the need for sustainability.
- 1987: Brundtland Report: Defined sustainable development as “meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.”
- 1992: Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro: Established the principles of sustainable development, including equity, intergenerational responsibility, and environmental protection.
- 2015: United Nations Sustainable Development Goals: Set ambitious targets for sustainable development, including goals related to SBE.
Key influential figures in the development of ethical principles in SBE include:
- Rachel Carson: Her book “Silent Spring” raised awareness of the environmental impacts of pesticides.
- Gro Harlem Brundtland: Former Prime Minister of Norway who chaired the World Commission on Environment and Development.
- Maurice Strong: Secretary-General of the 1992 Earth Summit.
- Ban Ki-moon: Former Secretary-General of the United Nations who promoted the Sustainable Development Goals.
2. Core Ethical Principles in SBE

SBE professionals are guided by a set of fundamental ethical principles that ensure ethical conduct and decision-making.
Key Principles
- Sustainability: Prioritizing the long-term well-being of the environment and society.
- Equity: Ensuring fair and just distribution of resources and benefits.
- Intergenerational Responsibility: Preserving the environment and resources for future generations.
- Precautionary Principle: Taking precautionary measures to prevent environmental harm even when scientific evidence is incomplete.
- Polluter Pays Principle: Holding those responsible for pollution accountable for its costs.
- Transparency and Accountability: Ensuring open and transparent decision-making and accountability for actions.
- Respect for Cultural Diversity: Valuing and respecting diverse cultural perspectives and practices.
3. Ethical Dilemmas and Challenges in SBE
SBE professionals face various ethical dilemmas and challenges in their work.
Common Dilemmas, History and ethical principles sbe
- Balancing economic development with environmental protection: Deciding how to prioritize these competing interests.
- Managing conflicts of interest: Ensuring that personal or financial interests do not influence professional decisions.
- Addressing social equity: Ensuring that SBE projects benefit all members of society, including marginalized groups.
- Responding to climate change: Deciding how to mitigate and adapt to the impacts of climate change.
Case Studies
- The Three Gorges Dam in China: A case study of the ethical challenges associated with large-scale infrastructure projects.
- The Deepwater Horizon oil spill: A case study of the ethical responsibilities of corporations in environmental disasters.
- The Dakota Access Pipeline: A case study of the ethical dilemmas surrounding the development of fossil fuel infrastructure.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the core ethical principles in SBE?
The core ethical principles in SBE include integrity, transparency, accountability, sustainability, and stakeholder engagement.
How can SBE professionals navigate ethical dilemmas?
SBE professionals can navigate ethical dilemmas by considering multiple perspectives, seeking guidance from professional codes of conduct, and consulting with experts or mentors.
What are the emerging ethical issues in SBE?
Emerging ethical issues in SBE include data privacy, artificial intelligence, sustainability, and cross-cultural ethical considerations.