Exercise 12.7 putting it all together to decipher earth history – Exercise 12.7, “Putting It All Together to Decipher Earth History,” embarks on a captivating journey to understand the intricate tapestry of our planet’s past. Through the meticulous examination of diverse geological evidence, scientists piece together the puzzle of Earth’s evolution, revealing a dynamic and ever-changing world.
Stratigraphy, the study of rock layers, provides a chronological framework for Earth’s history. Fossils, preserved remnants of ancient life, offer invaluable insights into past ecosystems and environments. Radiometric dating techniques unveil the age of rocks and minerals, enabling us to establish a timeline for geological events.
Plate tectonics, the theory of Earth’s moving crust, explains the distribution of rocks and fossils, shaping the planet’s surface and driving its evolution.
Introduction

Exercise 12.7 is a comprehensive exercise that provides a framework for understanding Earth’s history by combining multiple lines of evidence.
This exercise utilizes stratigraphy, fossils, radiometric dating, and plate tectonics to decipher past environments and events.
Stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is the study of rock layers and their relationships to understand the history of the Earth.
Principles of stratigraphy include the law of superposition, which states that younger layers are deposited on top of older layers, and the principle of lateral continuity, which states that rock layers extend laterally until they pinch out or are cut off by a fault.
- Rock units can be classified as formations, members, beds, and laminae based on their thickness and composition.
- Stratigraphy has been used to reconstruct past environments, such as the formation of the Grand Canyon and the movement of the continents.
Fossils, Exercise 12.7 putting it all together to decipher earth history
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of past life.
Different types of fossils include body fossils, trace fossils, and chemical fossils.
- Fossils can be used to date rocks and reconstruct past ecosystems, such as the use of trilobites to date the Paleozoic Era.
- The fossil record provides evidence for the evolution of life on Earth.
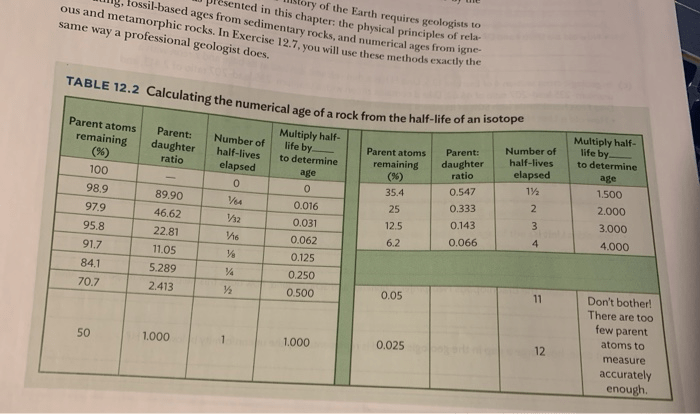
Radiometric Dating
Radiometric dating is a technique used to determine the age of rocks and minerals based on the decay of radioactive isotopes.
Different types of radiometric dating methods include potassium-argon dating, carbon-14 dating, and uranium-lead dating.
- Radiometric dating has been used to date the Earth to be approximately 4.54 billion years old.
- It has also been used to date specific rock formations and events, such as the age of the dinosaurs.
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics is the theory that the Earth’s lithosphere is divided into a number of tectonic plates that move around the globe.
Different types of plate boundaries include convergent boundaries, divergent boundaries, and transform boundaries.
- Plate tectonics has been used to explain the distribution of rocks and fossils on Earth, as well as the formation of mountain ranges and ocean basins.
- It has also been used to understand the history of the Earth’s climate and the evolution of life.
Putting it All Together
By combining the different types of evidence used in Exercise 12.7, scientists can create a comprehensive understanding of Earth’s history.
For example, stratigraphy can be used to determine the sequence of events in a particular area, while fossils can provide information about the organisms that lived during those events.
Radiometric dating can then be used to date the rocks and fossils, and plate tectonics can be used to explain the movement of the continents and the formation of mountain ranges.
FAQ Insights: Exercise 12.7 Putting It All Together To Decipher Earth History
What is the significance of Exercise 12.7?
Exercise 12.7 provides a comprehensive framework for understanding Earth’s history through the integration of diverse geological evidence, offering a holistic view of our planet’s evolution.
How does stratigraphy contribute to deciphering Earth’s history?
Stratigraphy establishes a chronological sequence of rock layers, providing a timeline for geological events and revealing past environments and depositional processes.
What role do fossils play in reconstructing Earth’s history?
Fossils, preserved remains of ancient organisms, provide direct evidence of past life and offer insights into the evolution of species, ecosystems, and environments.
How is radiometric dating used to determine the age of rocks?
Radiometric dating measures the decay of radioactive isotopes in rocks and minerals, providing precise ages for geological events and establishing a timeline for Earth’s history.
How does plate tectonics explain the distribution of rocks and fossils on Earth?
Plate tectonics, the theory of Earth’s moving crust, accounts for the distribution of rocks and fossils by explaining the formation and movement of tectonic plates, which shape the planet’s surface and drive geological processes.