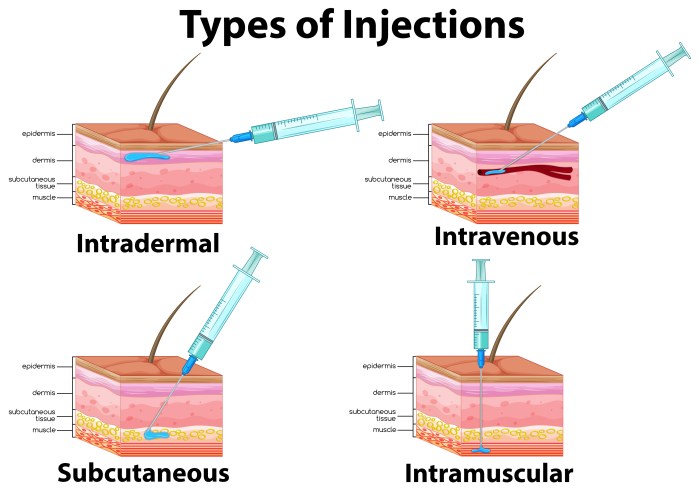
A nurse is preparing to give an intramuscular injection, a procedure that involves injecting medication into the muscle tissue. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the steps involved, ensuring the safe and effective administration of intramuscular injections.
Intramuscular injections are commonly used to deliver medications that require rapid absorption or have a prolonged duration of action. They are often administered in the deltoid, vastus lateralis, or gluteal muscles.
Preparing the Injection Site
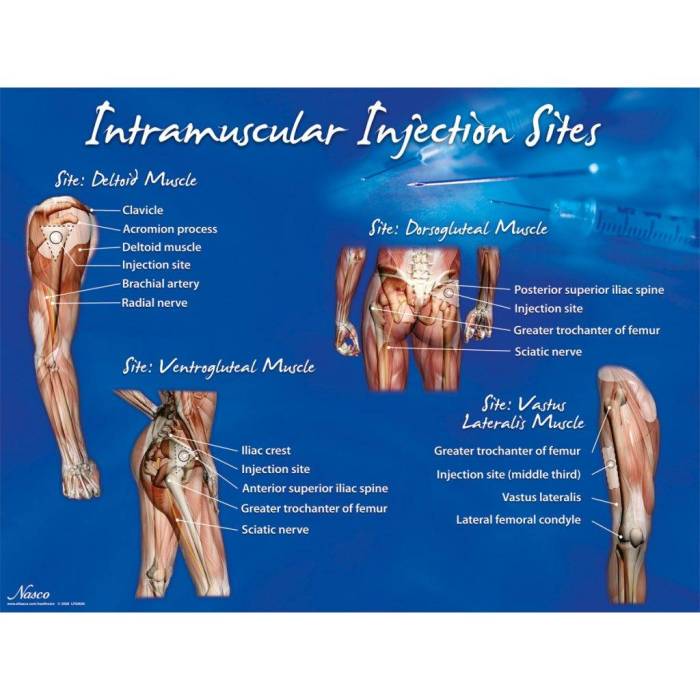
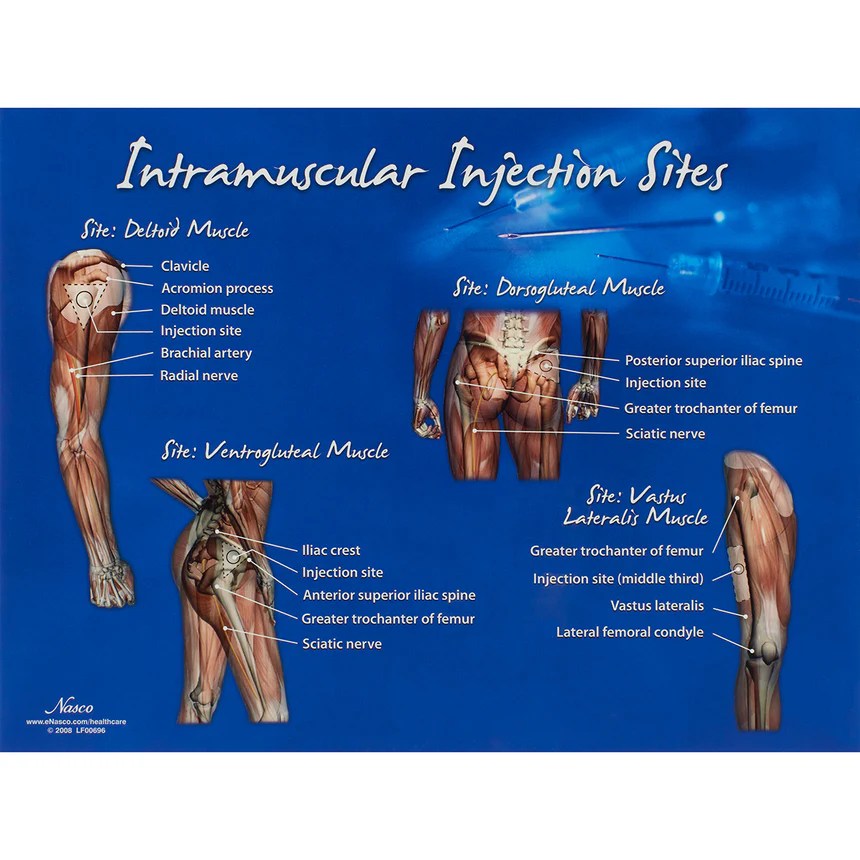
Selecting the appropriate injection site is crucial to ensure patient comfort and prevent complications. Common injection sites for intramuscular injections include the deltoid, ventrogluteal, dorsogluteal, and vastus lateralis muscles. Skin preparation is essential to reduce the risk of infection and includes cleaning the area with an antiseptic solution.
Common Injection Sites
- Deltoid muscle: Upper outer arm
- Ventrogluteal muscle: Upper outer quadrant of the buttocks
- Dorsogluteal muscle: Upper outer quadrant of the buttocks
- Vastus lateralis muscle: Outer thigh
Skin Preparation
Skin preparation involves cleaning the injection site with an antiseptic solution, such as alcohol or chlorhexidine. Allow the area to air dry completely before injecting.
Equipment and Supplies
| Equipment | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Syringe | Holds and delivers the medication |
| Needle | Pierces the skin and delivers the medication |
| Medication vial | Contains the medication |
| Alcohol swabs | Cleans the injection site |
| Gauze pads | Absorbs blood and prevents bleeding |
| Sharps container | Disposes of used needles and syringes |
Handling and Storage
Equipment should be handled with care and stored in a clean, dry place. Needles should never be recapped after use to prevent accidental needlesticks.
Medication Preparation: A Nurse Is Preparing To Give An Intramuscular Injection
Reconstituting Powdered Medications
Powdered medications require reconstitution before injection. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully, using the appropriate diluent and volume.
Dosage Calculation and Measurement
Accurate dosage calculation and measurement are essential to ensure patient safety. Use a calibrated syringe and measure the medication precisely.
Safe Handling and Storage
Medications should be handled and stored according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Protect medications from light, heat, and moisture.
Injection Technique

Z-Track Method
The Z-track method is used for intramuscular injections to prevent medication leakage and muscle damage. After inserting the needle, pull back slightly to create a small pocket. Inject the medication slowly and withdraw the needle at a 90-degree angle.
Needle Insertion
Insert the needle at a 90-degree angle to the skin. The depth of insertion depends on the muscle being injected and the length of the needle.
Aspiration
Before injecting the medication, aspirate slightly to check for blood. If blood is present, withdraw the needle and reposition it.
Patient Education and Monitoring
Pre-Injection Instructions
- Inform the patient about the procedure and potential side effects.
- Obtain consent for the injection.
- Position the patient comfortably.
Post-Injection Instructions
- Apply pressure to the injection site to stop bleeding.
- Monitor the patient for any adverse reactions.
- Provide written instructions on follow-up care.
Complications and Adverse Reactions
Potential complications and adverse reactions include pain, swelling, redness, bleeding, infection, and allergic reactions.
Patient Monitoring
Monitor the patient for at least 15 minutes after the injection for any adverse reactions.
Documentation and Evaluation
Essential Documentation
Essential documentation includes the date, time, injection site, medication administered, dosage, and any adverse reactions.
Importance of Accurate Documentation
Accurate and timely documentation ensures patient safety, legal protection, and continuity of care.
Ongoing Evaluation, A nurse is preparing to give an intramuscular injection
Ongoing evaluation of injection technique and patient outcomes is essential to ensure patient safety and efficacy.
FAQ
What is the purpose of skin preparation before an intramuscular injection?
Skin preparation helps to reduce the risk of infection by removing dirt and bacteria from the injection site.
What is the Z-track method?
The Z-track method is a technique used to prevent medication from leaking back out of the injection site. It involves pulling the skin and underlying tissue to one side before inserting the needle, then releasing the skin after the injection is complete.
What are potential complications of intramuscular injections?
Potential complications include pain, bleeding, infection, and nerve damage.