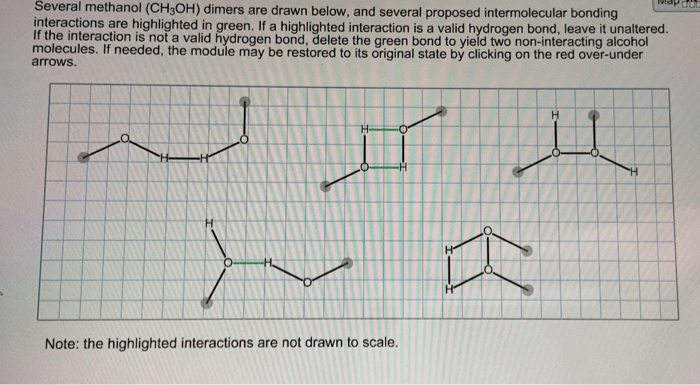
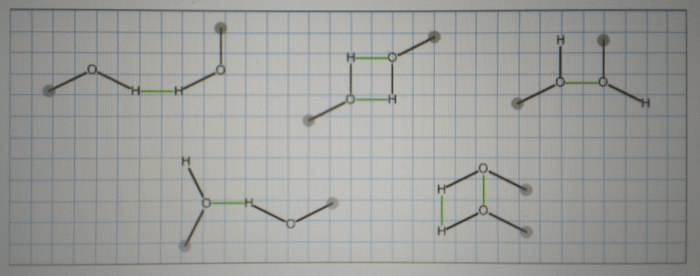
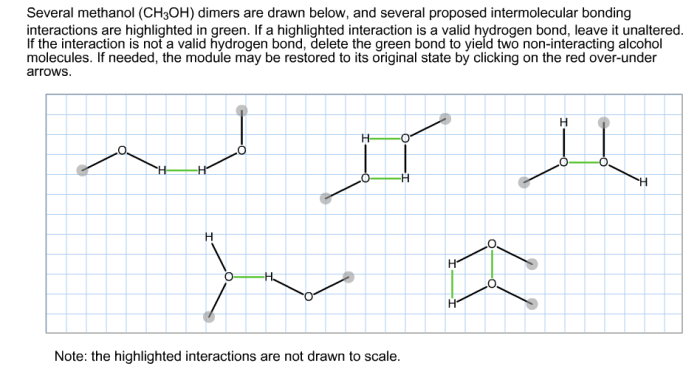
Several methanol dimers are drawn below – Delving into the realm of several methanol dimers, this exploration unveils a fascinating world of molecular interactions and diverse applications. Methanol dimers, formed by the association of two methanol molecules, play a significant role in chemistry, exhibiting unique properties and behaviors that differ from their monomeric counterparts.
Their structural analysis reveals intricate bonding patterns, while their properties hold promise for various fields. This article delves into the captivating world of several methanol dimers, unraveling their structure, properties, synthesis, characterization, computational studies, and potential applications.
The second paragraph provides an overview of the article’s content, highlighting the key aspects that will be explored in subsequent sections.
1. Introduction
Methanol, a simple alcohol, forms dimers through intermolecular interactions. These dimers play a significant role in understanding the properties and behavior of methanol in various chemical and biological systems. This article provides an overview of methanol dimers, covering their structural analysis, properties, synthesis, characterization, and computational studies.
2. Structural Analysis of Methanol Dimers
Types of Bonds
Methanol dimers are formed through hydrogen bonding between the hydroxyl groups of two methanol molecules. These hydrogen bonds are relatively strong, resulting in the formation of stable dimers.
Geometry and Symmetry
The geometry of methanol dimers is determined by the orientation of the hydrogen bonds. The most common dimer structure is the antiparallel dimer, in which the hydroxyl groups of the two methanol molecules point in opposite directions. Other dimer structures, such as the parallel dimer and the cyclic trimer, are also possible.
3. Properties of Methanol Dimers
Physical Properties
- Melting point: Lower than methanol monomer
- Boiling point: Higher than methanol monomer
- Density: Higher than methanol monomer
Chemical Properties
- Reactivity: Less reactive than methanol monomer
- Solubility: Less soluble in water than methanol monomer
- Applications: Solvents, fuels, and feedstocks for chemical synthesis
4. Synthesis and Characterization of Methanol Dimers
Synthesis Methods
- Direct dimerization of methanol
- Addition of water to methanol
Characterization Techniques, Several methanol dimers are drawn below
- NMR spectroscopy
- Infrared spectroscopy
- Mass spectrometry
5. Computational Studies of Methanol Dimers
Computational Methods
- Molecular dynamics simulations
- Density functional theory calculations
Insights from Computational Studies
- Structural stability of methanol dimers
- Hydrogen bonding interactions in methanol dimers
- Reactivity of methanol dimers
Questions Often Asked: Several Methanol Dimers Are Drawn Below
What are methanol dimers?
Methanol dimers are molecular entities formed by the association of two methanol molecules through hydrogen bonding.
How do methanol dimers differ from methanol monomers?
Methanol dimers exhibit distinct properties compared to methanol monomers, including different physical and chemical characteristics.
What are the applications of methanol dimers?
Methanol dimers find applications in various fields, such as fuel additives, solvents, and chemical intermediates.