Logical fallacies in The Crucible, a historical play by Arthur Miller, serve as a poignant reminder of the dangers of flawed reasoning and the devastating consequences that can ensue. Set against the backdrop of the Salem witch trials, the play vividly illustrates how logical fallacies can fuel mass hysteria, erode trust, and undermine justice.
The play’s plot revolves around the accusations of witchcraft that engulf the Puritan community of Salem, Massachusetts. As the accusations escalate, a series of logical fallacies are employed to justify the persecution of innocent individuals. These fallacies, ranging from ad hominem attacks to hasty generalizations, reveal the fragility of human reason when influenced by fear and prejudice.
Logical Fallacies in The Crucible
The Crucible, a play by Arthur Miller, serves as a potent allegory for the McCarthy era’s rampant logical fallacies and their devastating consequences. Set in 17th-century Salem, Massachusetts, the play explores the mass hysteria that gripped the community during the infamous witch trials, revealing how flawed reasoning and unchecked emotions can lead to injustice and tragedy.
Types of Logical Fallacies in The Crucible
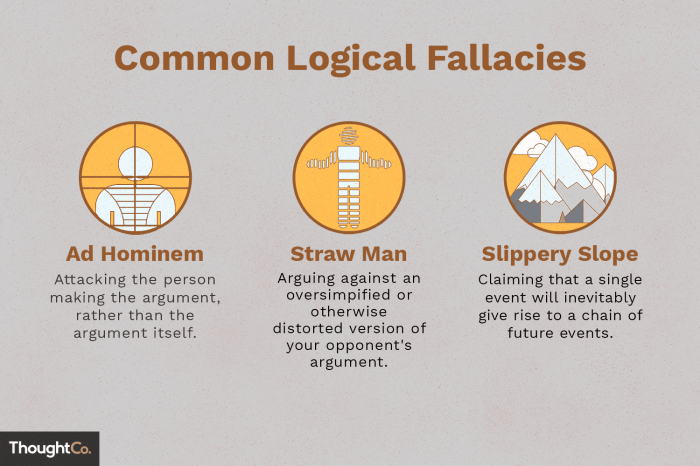
The play showcases a wide range of logical fallacies, including:
- Ad Hominem:Attacking an individual’s character rather than their argument (e.g., “You’re a witch because you’re a stranger”).
- Straw Man:Misrepresenting an opponent’s argument to make it easier to attack (e.g., “You say witchcraft is evil, but you don’t believe in God”).
- Slippery Slope:Exaggerating the potential consequences of an action to create fear (e.g., “If we don’t execute these witches, the Devil will take over Salem”).
Consequences of Logical Fallacies in The Crucible
The use of logical fallacies in The Crucible has dire consequences:
- Injustice:Innocent people are accused and executed based on faulty evidence.
- Erosion of Trust:Suspicion and paranoia spread throughout the community, destroying relationships.
- Division:The community is torn apart as accusations and counter-accusations fly.
Lessons Learned from Logical Fallacies in The Crucible
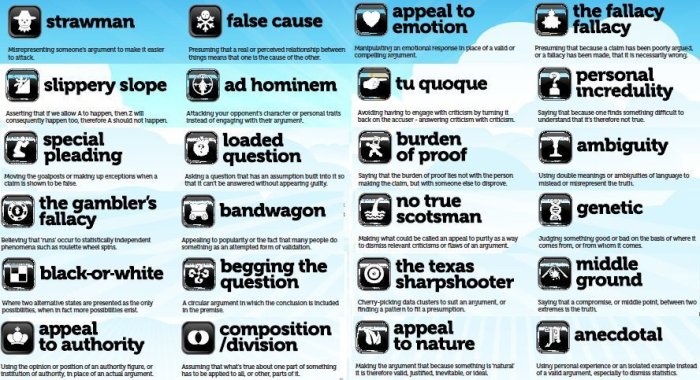
The play offers valuable lessons about the importance of critical thinking:
- Recognize and Avoid Fallacies:Understanding common logical fallacies helps us avoid being misled by them.
- Question Assumptions:Challenge the underlying assumptions behind arguments to uncover potential fallacies.
- Seek Evidence:Demand solid evidence to support claims before accepting them as true.
FAQ Insights
What is the significance of logical fallacies in The Crucible?
Logical fallacies in The Crucible play a crucial role in fueling the witch hunt and undermining justice. They provide a veneer of legitimacy to the accusations, swaying public opinion and silencing dissent.
How does the play illustrate the consequences of logical fallacies?
The play demonstrates how logical fallacies can lead to the erosion of trust, the persecution of innocent individuals, and the collapse of social order.
What lessons can we learn from the logical fallacies in The Crucible?
The play teaches us the importance of critical thinking, the need to question assumptions, and the dangers of allowing fear and prejudice to cloud our judgment.



