Lab activity latitude and longitude is a foundational concept in geography that allows us to precisely locate and navigate the Earth’s surface. Latitude and longitude are two angular coordinates that define the position of any point on the globe, providing a systematic framework for understanding the Earth’s spatial relationships.
This engaging lab activity introduces students to the concepts of latitude and longitude, the instruments used to measure them, and their practical applications in various fields. Through hands-on activities and real-world examples, students will gain a deeper understanding of these essential coordinates and their significance in mapping, navigation, and scientific exploration.
Overview of Latitude and Longitude
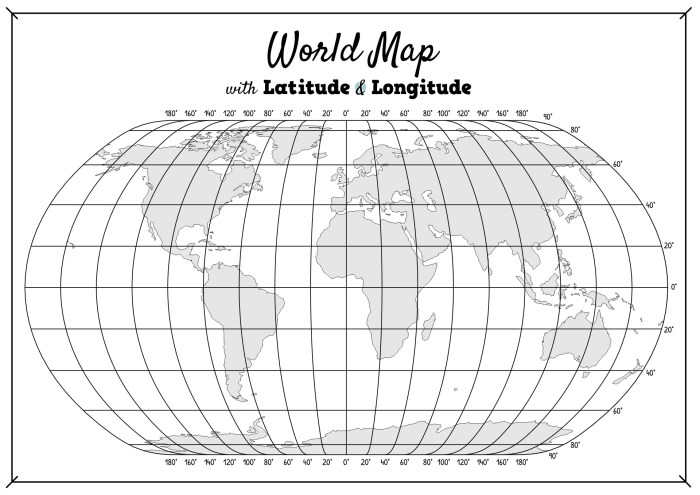
Latitude and longitude are geographic coordinate systems that define the location of a point on the Earth’s surface. Latitude measures the angular distance north or south of the Equator, while longitude measures the angular distance east or west of the Prime Meridian.
Latitude and longitude lines form a grid that can be used to locate any point on the Earth’s surface. Latitude lines are parallel to the Equator, and longitude lines are perpendicular to the Equator. The Equator is the line of latitude at 0 degrees, and the Prime Meridian is the line of longitude at 0 degrees.
Latitude and longitude are essential for navigation and mapping. They are also used in a variety of other applications, such as weather forecasting, climate modeling, and land surveying.
Visual Representation, Lab activity latitude and longitude
The following diagram shows a globe with latitude and longitude lines.
[Image of a globe with latitude and longitude lines]
The Equator is shown as a red line, and the Prime Meridian is shown as a blue line. The other latitude and longitude lines are shown as black lines.
Measuring Latitude and Longitude
Determining the precise location of a point on Earth’s surface requires measuring its latitude and longitude. Latitude measures the angular distance north or south of the equator, while longitude measures the angular distance east or west of the prime meridian.
Instruments Used
- Sextant:A handheld instrument used to measure the angle between the horizon and a celestial body (e.g., the sun or a star).
- Astrolabe:A historical instrument that measures the altitude of celestial bodies above the horizon.
- GPS Receiver:A modern device that uses satellite signals to determine its position on Earth.
Methods for Determining Latitude
Latitude can be determined by measuring the angle of elevation of the sun or a star above the horizon. The angle is then converted to latitude using trigonometric calculations.
Methods for Determining Longitude
Longitude is determined by comparing the local time to the time at a reference meridian (e.g., the prime meridian). The difference in time corresponds to the difference in longitude.
Real-World Examples
- Navigation:Latitude and longitude are essential for marine and air navigation, allowing vessels and aircraft to accurately determine their position and course.
- Mapping:Latitude and longitude provide a framework for creating maps and charts, enabling precise location identification.
- Surveying:Latitude and longitude are used to establish property boundaries, conduct land surveys, and create topographic maps.
Applications of Latitude and Longitude
Latitude and longitude are essential geographic coordinates used in various fields, providing a precise system for locating and navigating across the globe.
In cartography, latitude and longitude form the basis of maps, enabling accurate representation of locations and distances on flat surfaces. They facilitate precise measurements and calculations of distances, areas, and directions, essential for mapmaking and navigation.
Navigation
Latitude and longitude are indispensable for navigation, both on land and sea. They allow navigators to determine their exact position and plan their course accordingly. GPS devices, compasses, and other navigation tools rely heavily on these coordinates to provide accurate guidance.
Ships and aircraft use latitude and longitude to chart their routes and ensure safe and efficient travel. By knowing their coordinates, navigators can avoid obstacles, determine their distance from destinations, and communicate their location to others.
Global Positioning Systems (GPS)
GPS is a satellite-based navigation system that utilizes latitude and longitude to pinpoint locations on Earth. GPS receivers receive signals from a constellation of satellites orbiting the planet, allowing them to calculate their precise position, altitude, and time.
GPS has revolutionized navigation, providing real-time location data for various applications, including navigation, surveying, and disaster response. It has also paved the way for location-based services, such as mapping apps, ride-sharing, and asset tracking.
Latitude and Longitude in Science and Exploration
Latitude and longitude have played a pivotal role in scientific research and exploration, providing a precise and universal reference system for mapping and understanding the Earth and its phenomena.
Tracking Animal Migrations
Latitude and longitude coordinates are crucial for tracking the movements and migration patterns of animals. By equipping animals with GPS devices or radio tags that record their location, scientists can monitor their journeys over vast distances and across different habitats.
This data helps researchers study animal behavior, population dynamics, and the impact of environmental factors on migration patterns.
Studying Weather Patterns
Latitude and longitude are essential for studying weather patterns and climate change. Weather stations and satellites use these coordinates to pinpoint the location of weather systems, such as storms, hurricanes, and jet streams. By tracking the movement of these systems, meteorologists can predict their path and intensity, enabling timely warnings and emergency preparedness.
Exploring New Territories
Latitude and longitude have been instrumental in the exploration of new territories throughout history. Explorers and navigators used these coordinates to chart unknown seas and lands, creating maps that guided subsequent expeditions and trade routes. Today, latitude and longitude continue to guide scientific expeditions, such as deep-sea exploration and space missions.
Historical Examples
Numerous scientific discoveries have been made possible by the use of latitude and longitude. For example, the famous voyage of the HMS Beagle, led by Charles Darwin, relied on accurate longitude measurements to determine the ship’s position during its groundbreaking exploration of the Galapagos Islands.
Latitude and Longitude in Education: Lab Activity Latitude And Longitude
Understanding latitude and longitude holds significant educational value, providing a framework for students to comprehend global geography and spatial relationships. Incorporating these coordinates into geography lessons enables them to grasp the world’s diverse physical and cultural landscapes, fostering a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of our planet.
Activities and Projects for Teaching Latitude and Longitude
Interactive activities and engaging projects can enhance students’ understanding of latitude and longitude. Here are a few examples:
- Latitude and Longitude Scavenger Hunt:Students use a map or globe to find specific locations based on their latitude and longitude coordinates, fostering their problem-solving and map-reading skills.
- Create a Latitude and Longitude Grid:Students draw a grid on a map or globe, labeling the latitude and longitude lines, which helps them visualize and understand the coordinate system.
- Latitude and Longitude in Real-Life Scenarios:Students explore real-life applications of latitude and longitude, such as navigation, weather forecasting, and understanding global events, demonstrating the practical relevance of these concepts.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
Latitude measures the distance north or south of the Equator, while longitude measures the distance east or west of the Prime Meridian.
How are latitude and longitude measured?
Latitude is measured using a sextant or GPS device, while longitude is measured using a chronometer or GPS device.
What are some real-world applications of latitude and longitude?
Latitude and longitude are used in navigation, cartography, surveying, and scientific research.